Posted inCardiology news Psychiatry
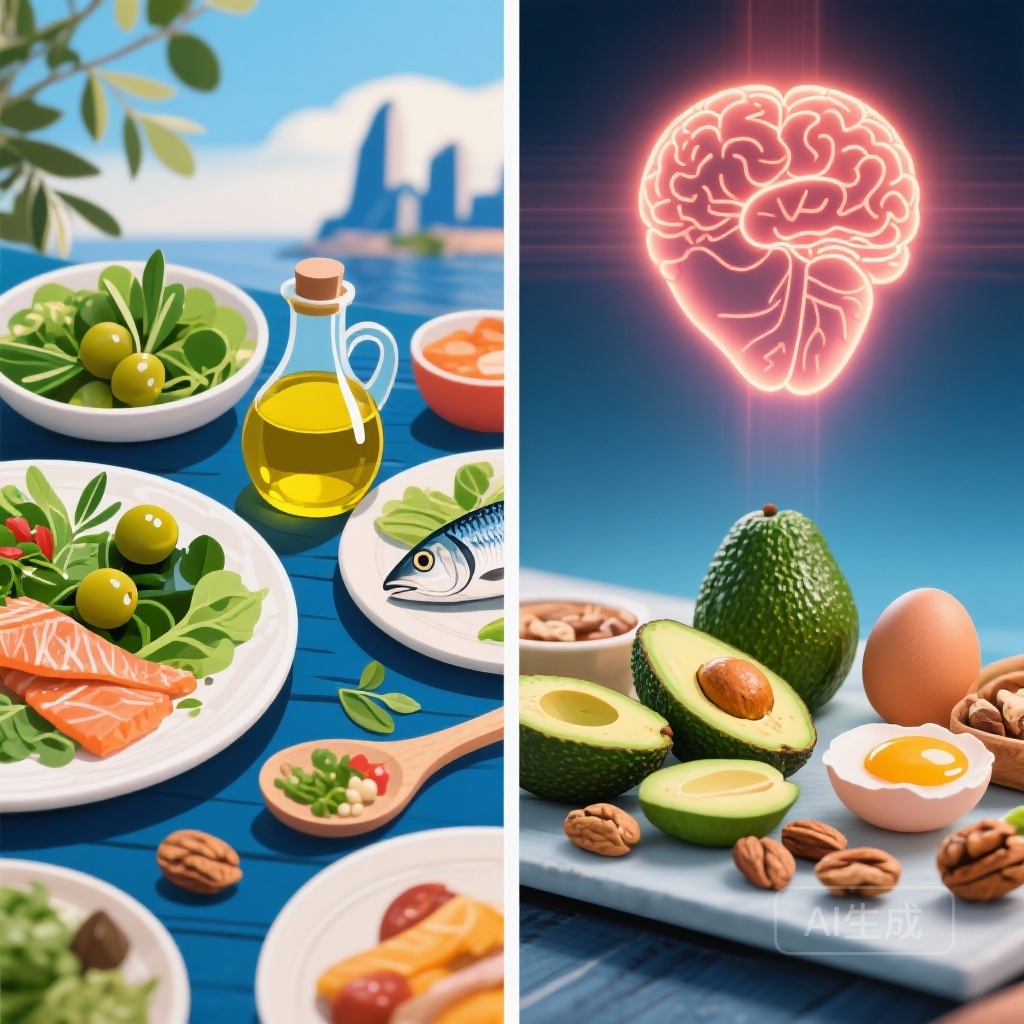
Keto vs. Mediterranean: New Evidence on Which Diet Wins for Heart and Brain Health
This article compares the Ketogenic and Mediterranean diets' impact on cardiovascular markers and mental health, highlighting results from two recent pilot studies on blood pressure and the gut-brain axis.