Posted inDiabetes & Endocrinology news Specialties
Orforglipron: A Promising Oral GLP-1 Receptor Agonist for Long-Term Obesity Management
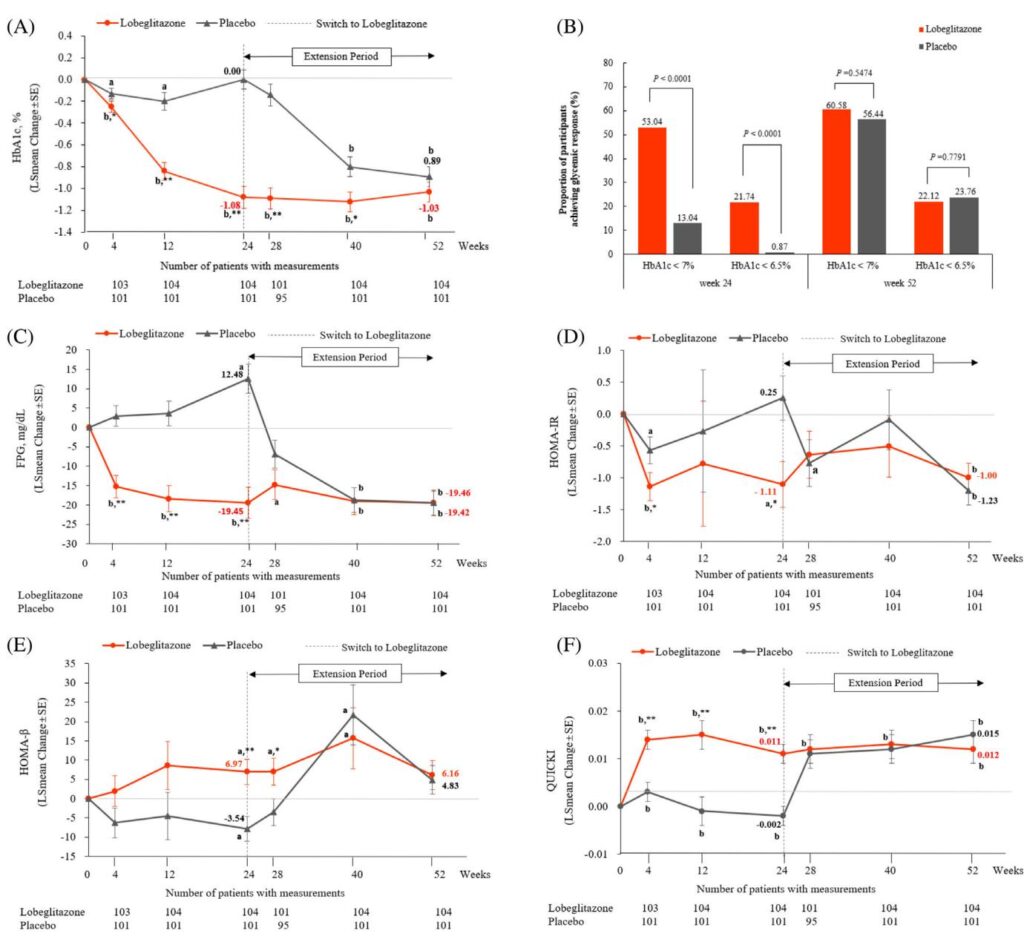
Orforglipron, a novel oral GLP-1 receptor agonist, demonstrated significant and sustained weight reduction in obese adults without diabetes in a 72-week phase 3 trial, with a tolerable safety profile consistent with existing GLP-1 therapies.