Posted inCardiology Infectious Diseases news
RSV-Related Hospitalization Linked to Surge in Acute Myocardial Infarction and Stroke Risk
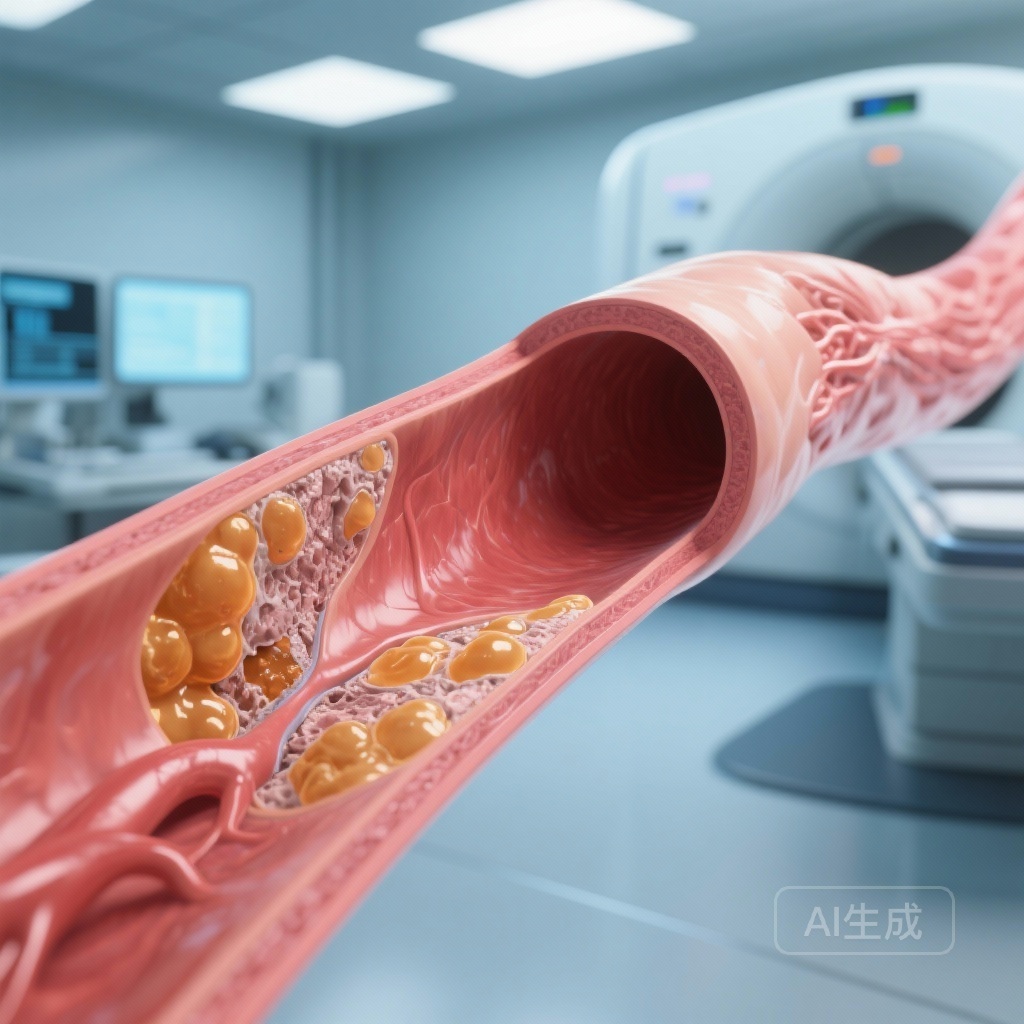
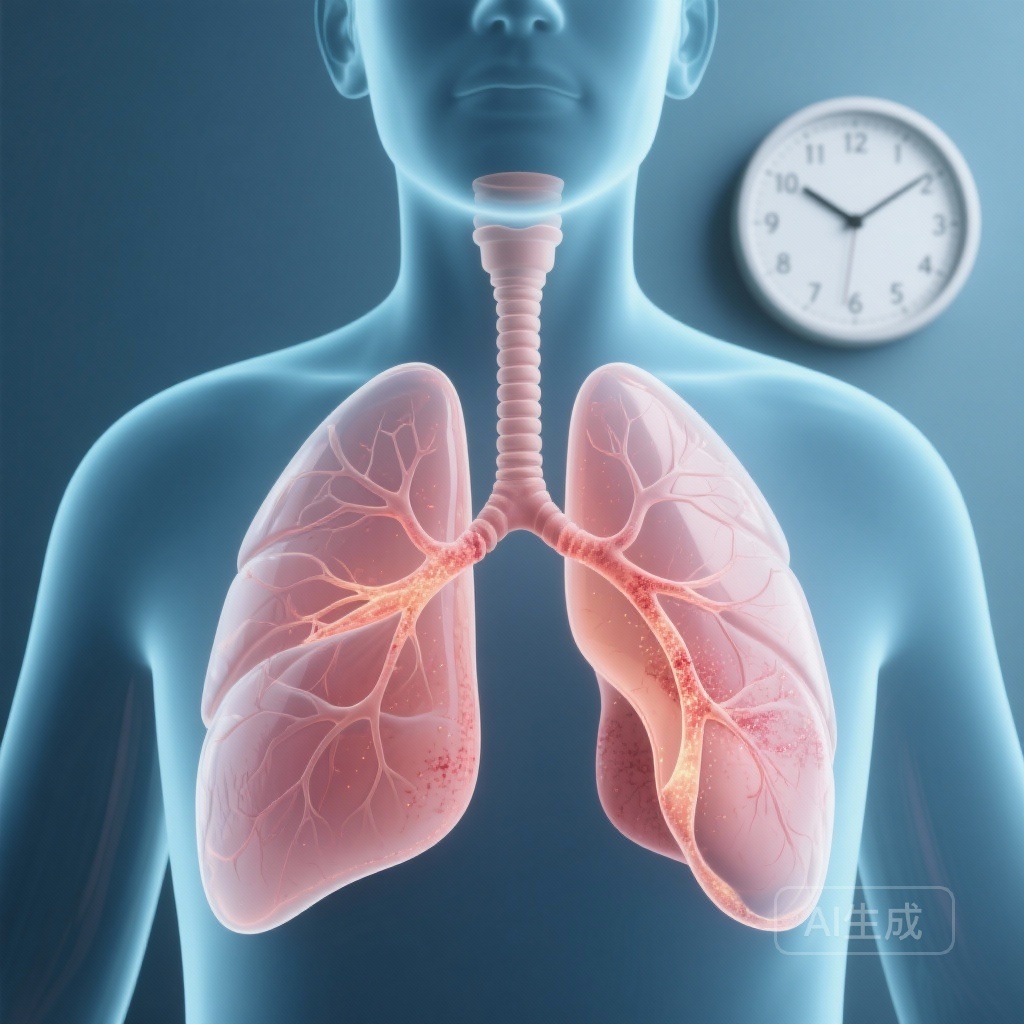
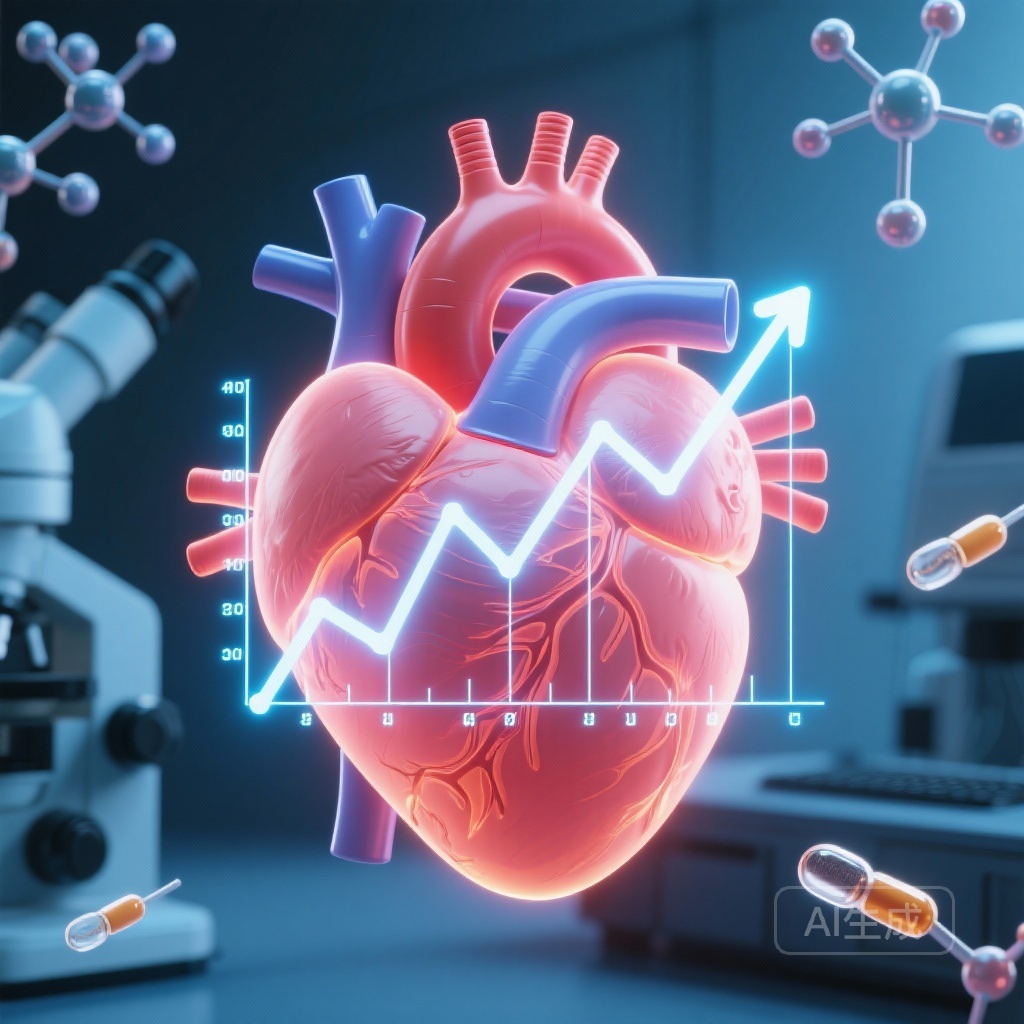
A large-scale study reveals that RSV hospitalization significantly increases the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and heart failure exacerbations, with the highest risk occurring within the first week post-admission, emphasizing the critical need for adult vaccination.