Posted innews Oncology Public Health
High, Persistent Breast Cancer Mortality in Sub‑Saharan Africa: 7‑Year ABC‑DO Cohort Reveals Major Survival Gaps and Actionable Targets
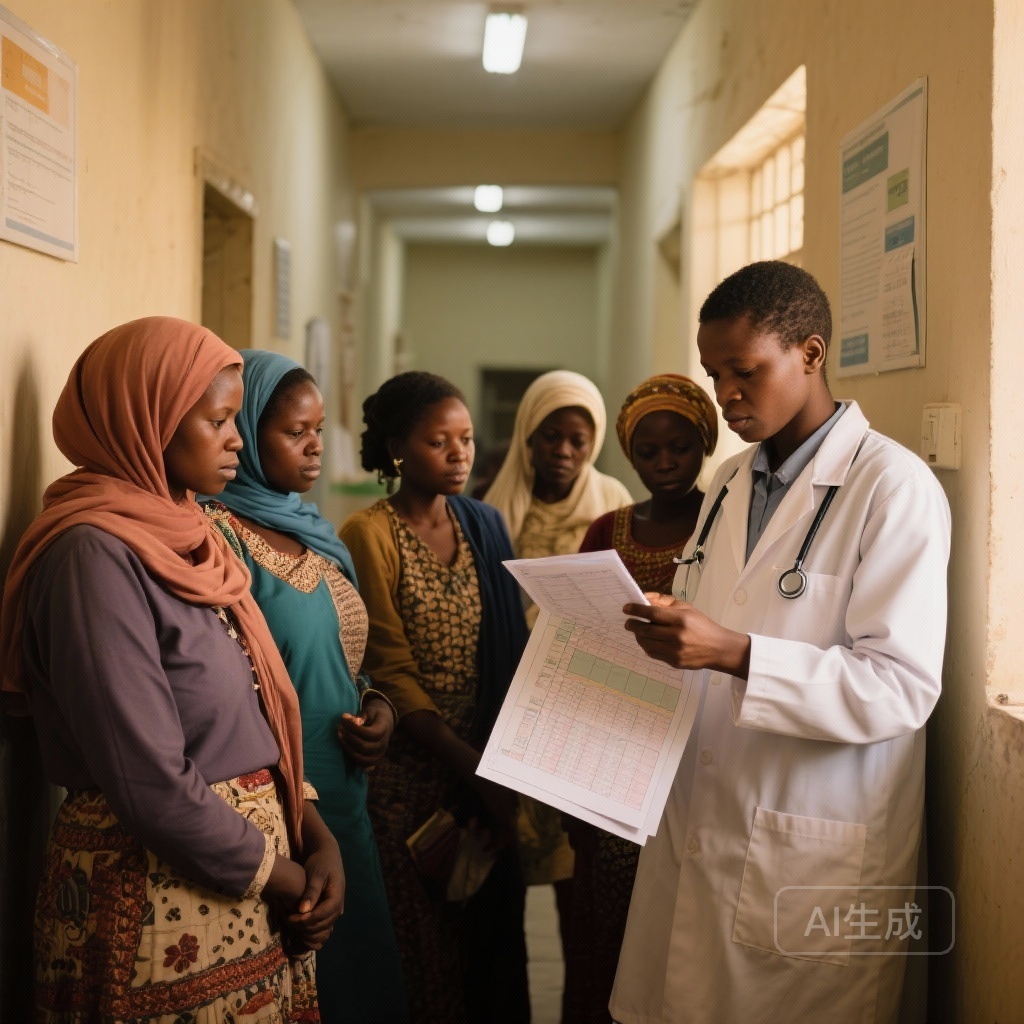
A 7‑year follow-up of 2,153 women in the ABC‑DO cohort shows poor breast cancer survival in much of sub‑Saharan Africa, with 5‑year crude survival 40% and marked between-country and racial disparities; reaching WHO stage downstaging targets and improving treatment access could cut deaths by about a third.