Posted inAnesthesiology Critical Care news
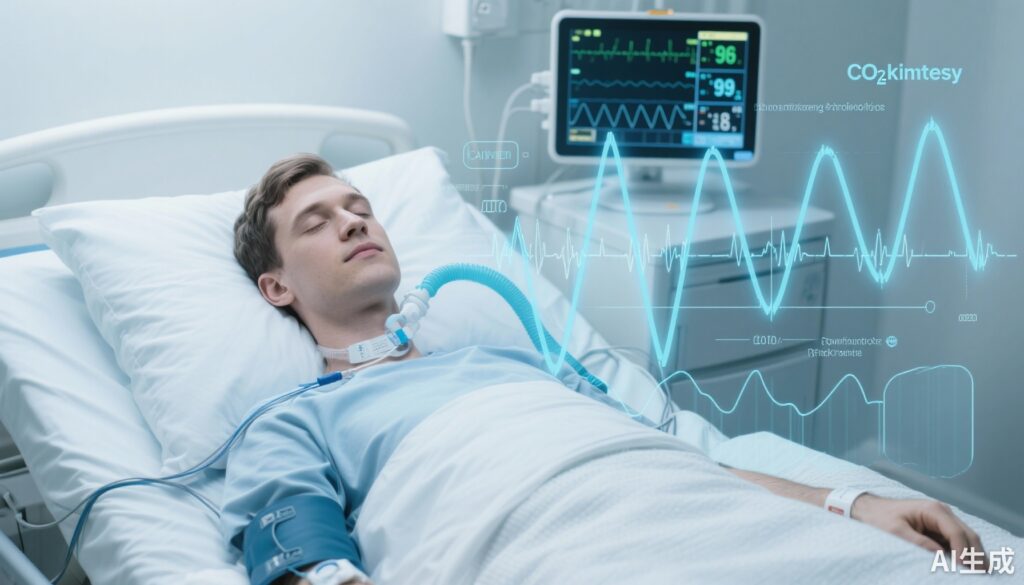
Continuous Intravenous Sedation Produces Novel EEG ‘Ups’ in Early Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure — Implications for Monitoring and Outcomes
In mechanically ventilated patients with early acute hypoxemic respiratory failure, continuous IV sedation produces EEG patterns (EEG Ups) not seen in natural sleep; these patterns correlate with sedation dose, drug combinations, clinical sedation depth, and ICU mortality.







![[Lutetium-177]Lu-PSMA-617 Delays Quality-of-Life Decline, Pain Progression, and Symptomatic Skeletal Events in PSMA-Positive mCRPC: In-depth PSMAfore Analysis](https://news.medxy.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/9d3c0201-d1b3-49f2-a408-3ea3d0347451-1024x585.jpg)