Medium‑Chain Triglyceride–Supplemented Ketogenic Diet in Parkinson’s Disease: A Small Randomized Feasibility Trial and What It Means for Clinical Practice
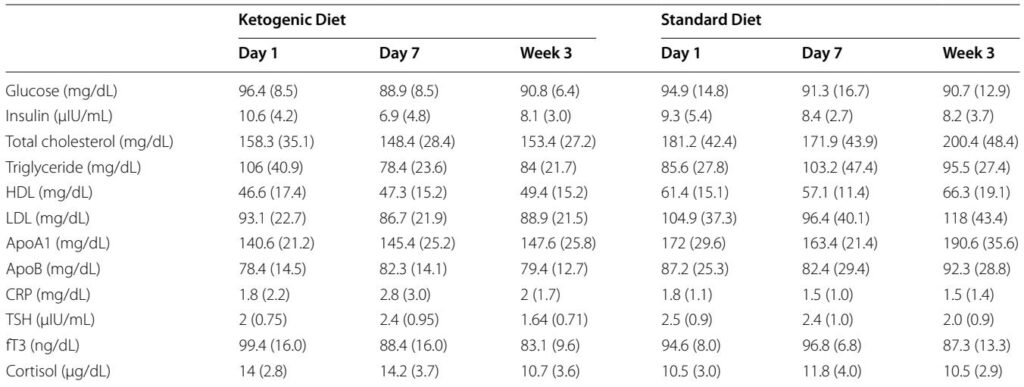
A randomized, double‑blind pilot tested an MCT‑supplemented ketogenic diet (MCT‑KD) in 16 people with moderate Parkinson’s disease. The diet was feasible and acceptable, induced nutritional ketosis by day 4, produced metabolic benefits and nonmotor symptom improvement, but did not change a primary mobility endpoint (TUG) over three weeks.