Posted inEmergency Medicine news Orthopedics
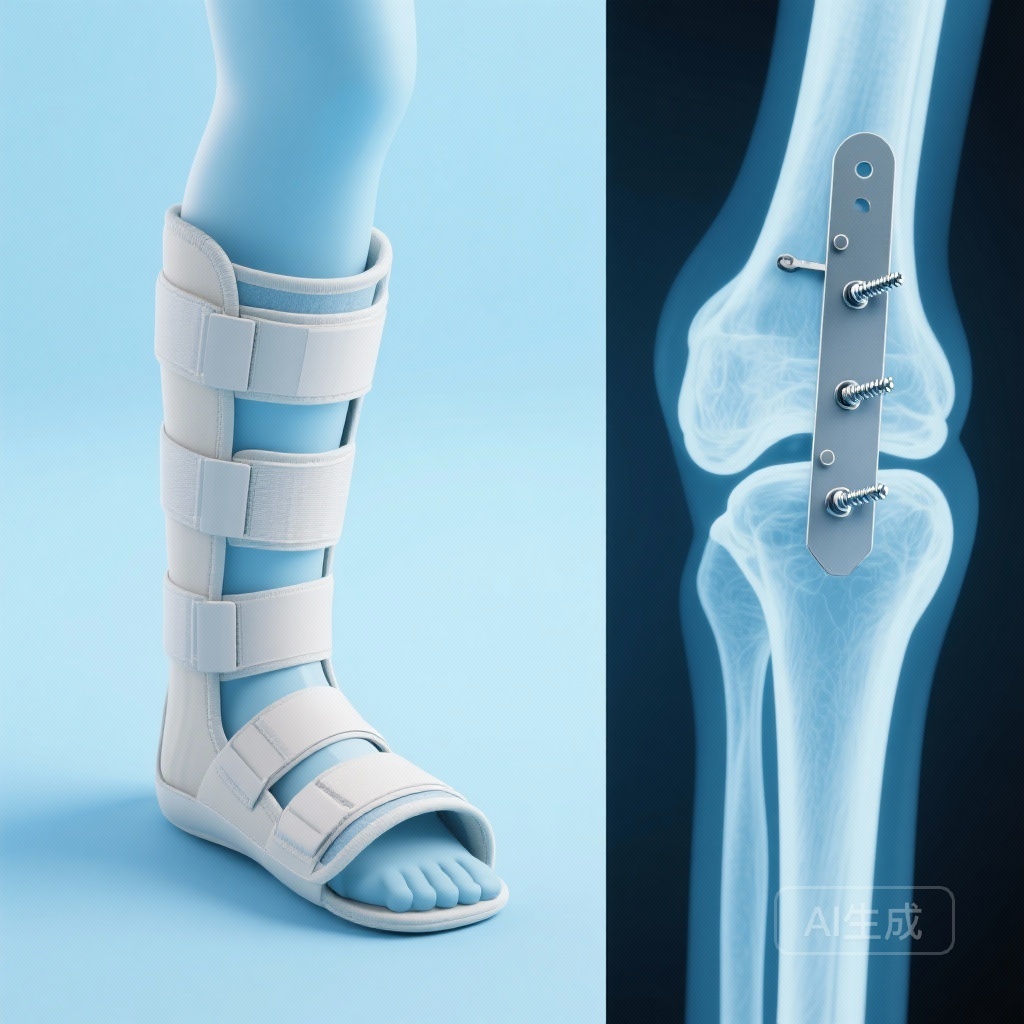
Cast Immobilization is Non-inferior to Surgery for Unstable Weber B Ankle Fractures: Results from the SUPER-FIN Trial
The SUPER-FIN randomized trial reveals that cast immobilization is a viable, non-inferior alternative to surgery for unstable Weber B ankle fractures with a congruent mortise, leading to fewer complications and avoiding unnecessary hardware removal procedures.