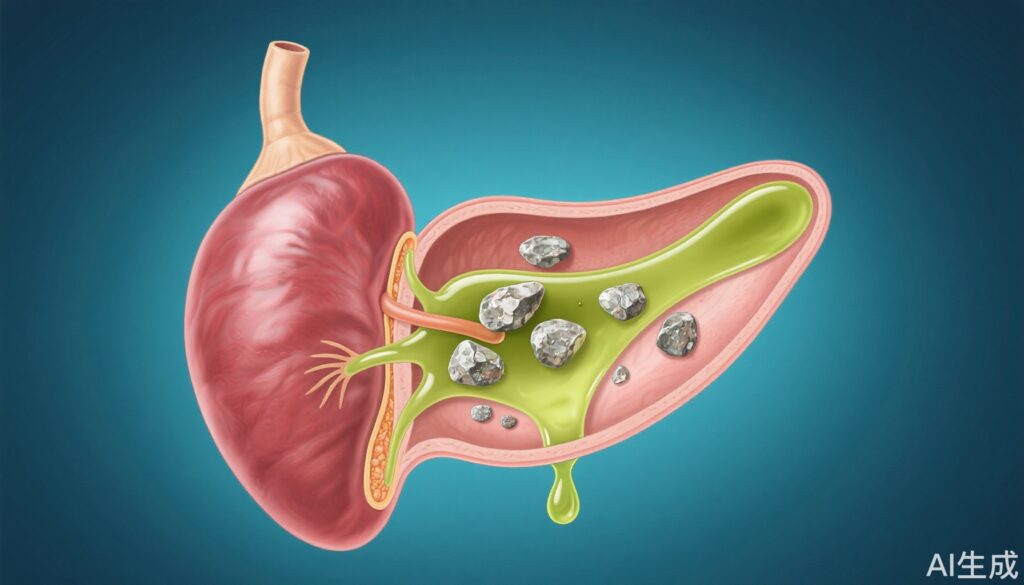
What Are Gallstones and How Do They Form?
The gallbladder is a small organ that stores bile—a digestive fluid produced by the liver. When bile components, such as cholesterol, increase in concentration, they can crystallize and form gallstones. These stones develop gradually, particularly in individuals over 40, with higher risks observed in women and those with obesity.
Does Skipping Breakfast Increase Risk?
A common belief is that skipping breakfast may contribute to gallstone formation. During sleep, bile accumulates in the gallbladder. Without food intake in the morning to prompt its release, bile can become overly concentrated, potentially leading to crystal formation over time. While skipping breakfast doesn’t guarantee gallstones, maintaining regular eating habits may help reduce the risk.
Why Don’t All Gallstones Cause Pain?
While gallstones are often associated with sharp abdominal pain, not all stones cause discomfort. Pain, or biliary colic, typically occurs when a stone obstructs bile flow. Some individuals discover gallstones incidentally during routine health checks because their stones do not block bile flow and remain symptomless.
Should You Remove Your Gallbladder?
Surgical removal of the gallbladder is a common treatment for symptomatic gallstones. However, there’s debate regarding asymptomatic cases. Some argue that proactive removal prevents complications like acute biliary infections, especially as surgery becomes riskier with age. Others suggest that in cases without symptoms, surgery might be unnecessary. Current medical guidelines recommend laparoscopic gallbladder removal as the standard treatment when symptoms are present.
Can Stones Be Removed Without Removing the Gallbladder?
Procedures that remove stones while preserving the gallbladder have been explored. However, these methods often result in high recurrence rates, and subsequent surgeries may involve more complications. Currently, such approaches are reserved for emergency scenarios.
How to Prevent Gallstones
Preventing gallstones involves lifestyle adjustments:
1. **Eat Regularly, Including Breakfast**: Regular meals prevent bile stagnation.
2. **Maintain a Balanced Diet**: Consume less fat and sugar, and more fruits and vegetables.
3. **Stay Active After Meals**: Light activity aids bile flow.
4. **Lose Weight Gradually**: Avoid extreme dieting, as it can disrupt bile secretion.
By adopting these habits, you can support gallbladder health and reduce the likelihood of gallstones forming.