Introduction
The soleus muscle, often referred to as the body’s second heart, plays a vital role in maintaining metabolic and cardiovascular health. This underappreciated muscle, located in the lower leg, is essential for effective blood circulation and glucose regulation. Recent research has highlighted its significance in improving blood sugar levels, reducing fat storage, and supporting overall cardiovascular function. This article explores the scientific evidence behind the soleus muscle’s role, practical exercises to optimize its performance, and how it can be a game-changer for individuals aiming to improve their health.
Background
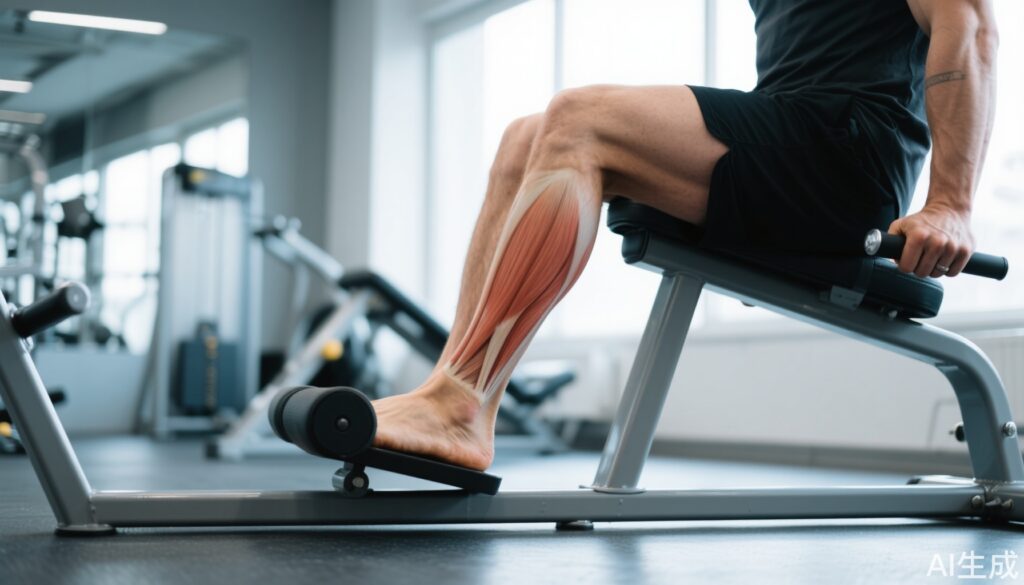
The soleus muscle is a powerful endurance muscle situated beneath the gastrocnemius, forming part of the calf. Unlike other muscles, it can sustain prolonged activity without fatigue, making it a key component in low-intensity movements such as walking or standing. Its unique ability to utilize blood glucose directly, bypassing the reliance on liver glycogen, positions it as a crucial player in maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Prof. Marc Hamilton and his research team at the University of Houston have brought this muscle into the spotlight by developing a specialized exercise called the Soleus Push-Up (SPU). This innovation targets the soleus to enhance its metabolic activity significantly. Published in the journal “iScience,” their findings suggest that activating the soleus muscle can outperform popular methods like intermittent fasting or high-intensity exercise in improving metabolic health.
Scientific and Clinical Evidence: What the Data Tell Us
Research highlights the soleus muscle’s ability to improve glucose metabolism. By continuously engaging this muscle, studies indicate a marked improvement in blood glucose utilization and a reduction in triglyceride levels in the bloodstream. The SPU exercise, specifically, has shown to double the rate of fat metabolism during fasting periods between meals.
Moreover, the soleus functions as a secondary blood pump, aiding venous return from the lower body to the heart. This mechanism helps prevent issues such as varicose veins and lower limb swelling, emphasizing its nickname “the second heart.”
Misconceptions and Harmful Behaviors
Many people underestimate the importance of low-intensity, sustained muscle activity in their fitness routines. The focus is often on high-intensity workouts, which, while beneficial, do not engage the soleus muscle in the same sustained manner. Additionally, sedentary lifestyles can lead to atrophy of this muscle, diminishing its capacity to regulate blood sugar and support cardiovascular health.
Correct Health Practices and Practical Exercises
To harness the benefits of the soleus muscle, it’s crucial to incorporate specific exercises into daily routines:
1. **Soleus Push-Up (SPU):** While sitting, raise your heels off the ground while keeping the front of the foot stationary. Hold for a few seconds before lowering back down. Repeat for several minutes.
2. **Seated Heel Raises:** Using weights for added resistance, this exercise targets the soleus efficiently. Sit with your knees bent at 90 degrees, place a weight on your thighs, and lift your heels slowly.
3. **Standing Heel Raises:** Perform these on a step for a greater range of motion. Lower your heels below the step edge and then lift as high as possible.
Expert Recommendations and Insights
Health professionals recommend integrating these exercises into daily routines, especially for individuals with metabolic disorders such as prediabetes. Incorporating these exercises can significantly improve glucose utilization and may prevent the progression of metabolic diseases. Moreover, stretching and foam rolling post-exercise are advised to prevent muscle stiffness and promote recovery.
Patient Scenario
Consider Jane, a 45-year-old office worker with a sedentary lifestyle and a family history of type 2 diabetes. After incorporating SPU and seated heel raises into her daily routine, she noticed improved energy levels and a reduction in her fasting blood glucose levels within a few weeks. This simple intervention became a cornerstone of her health improvement strategy.
Conclusion
The soleus muscle, often overlooked, holds the key to significant metabolic and cardiovascular benefits. By engaging this muscle through specific low-intensity exercises, individuals can improve blood sugar regulation, enhance fat metabolism, and support overall cardiovascular health. Incorporating these practices into daily routines offers a practical, accessible way to enhance long-term health.
References
1. Elek D, Tóth M, Sonkodi B, Ács P, Kovács GL, Tardi P, Melczer C. The Efficacy of Soleus Push-Up in Individuals with Prediabetes: A Pilot Study. Sports (Basel). 2025 Mar 10;13(3):81. doi: 10.3390/sports13030081. PMID: 40137805; PMCID: PMC11946342.