Posted inCardiology news Radiology Specialties
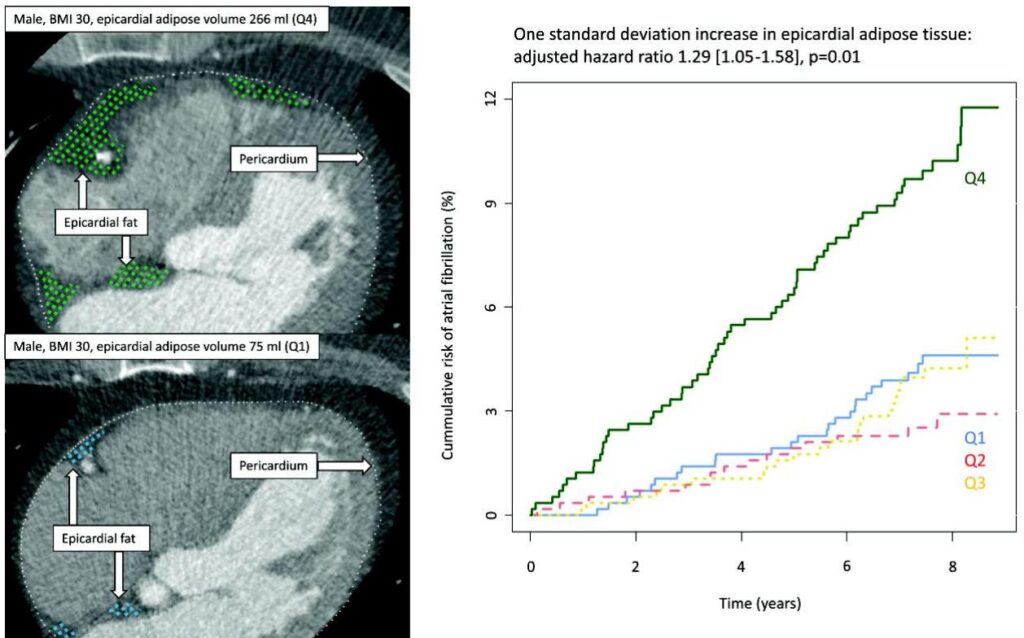
Epicardial Adipose Tissue as a Predictor of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation: Insights from a Danish Population Cohort
This Danish cohort study demonstrates that increased epicardial adipose tissue volume independently elevates the risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation, highlighting the importance of fat distribution beyond BMI in cardiovascular risk assessment.