Posted inGastroenterology Infectious Diseases news
Not All ‘Indeterminate’ HBV Is Equal: Specific Indeterminate Types Carry Markedly Higher Long‑Term HCC Risk
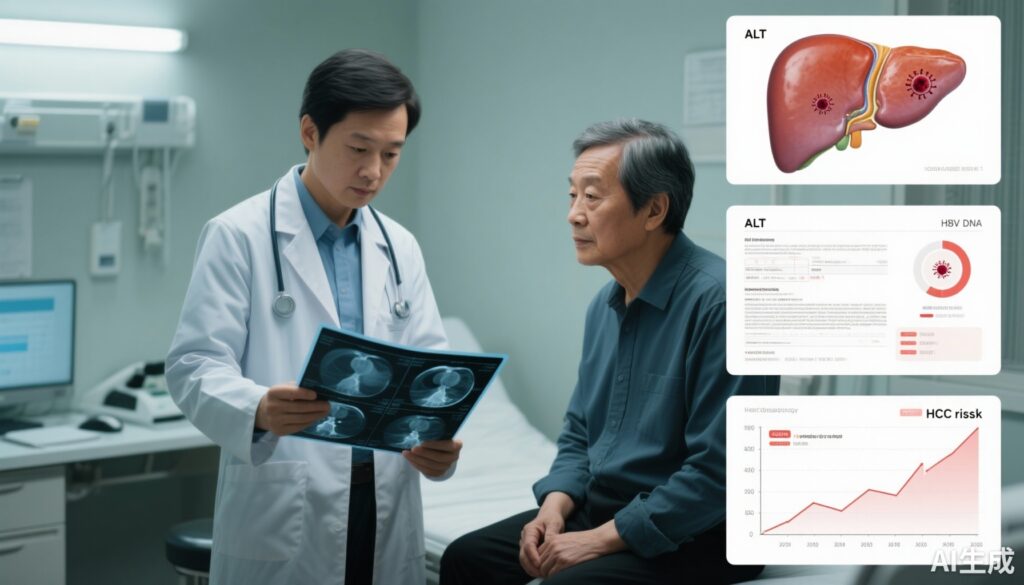
A multinational cohort study of 1,986 patients with indeterminate chronic hepatitis B (CHB) shows large differences in long‑term hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) risk by baseline indeterminate subtype and by phase transition, identifying subgroups that may benefit from earlier antiviral therapy and intensified surveillance.