Posted inInfectious Diseases Neurology news
Beyond the Fever: Acute Dengue Infection Linked to Significant Neurological Risks in Older Adults
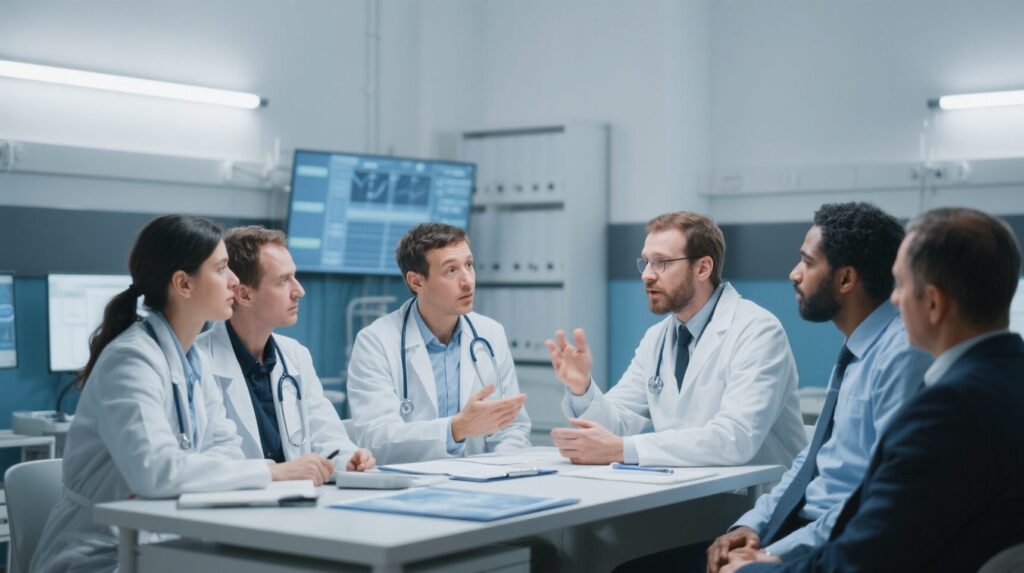
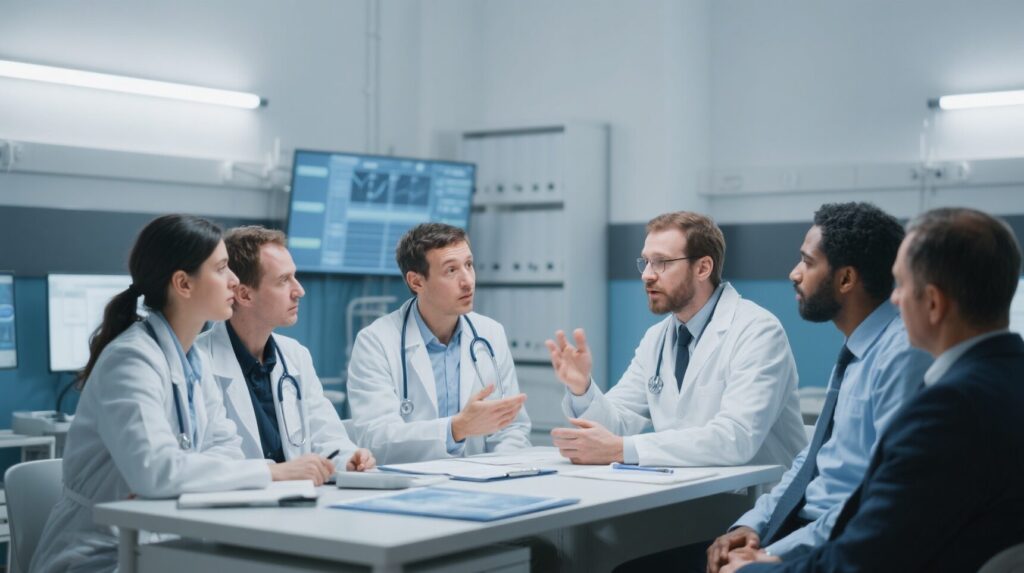
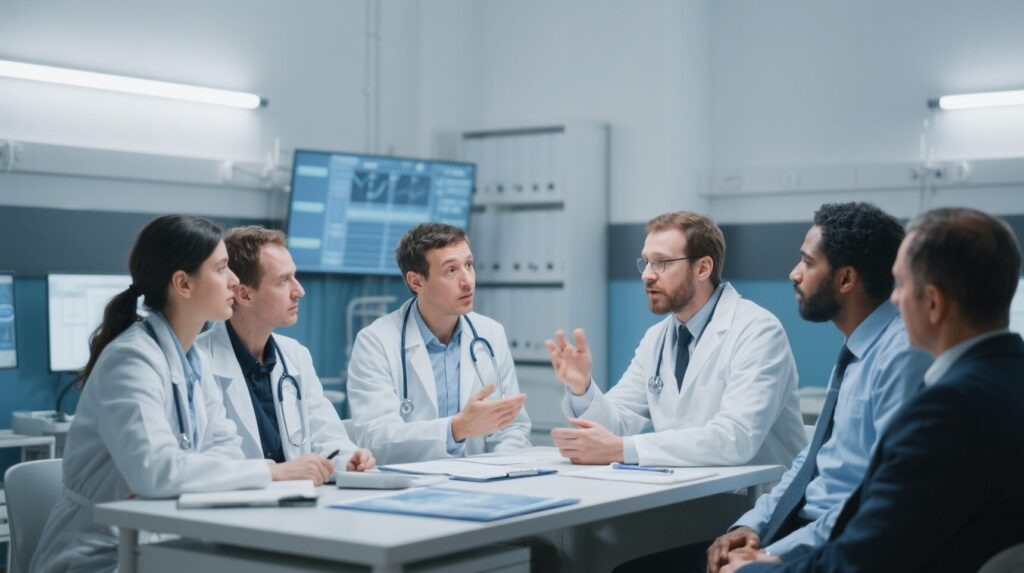
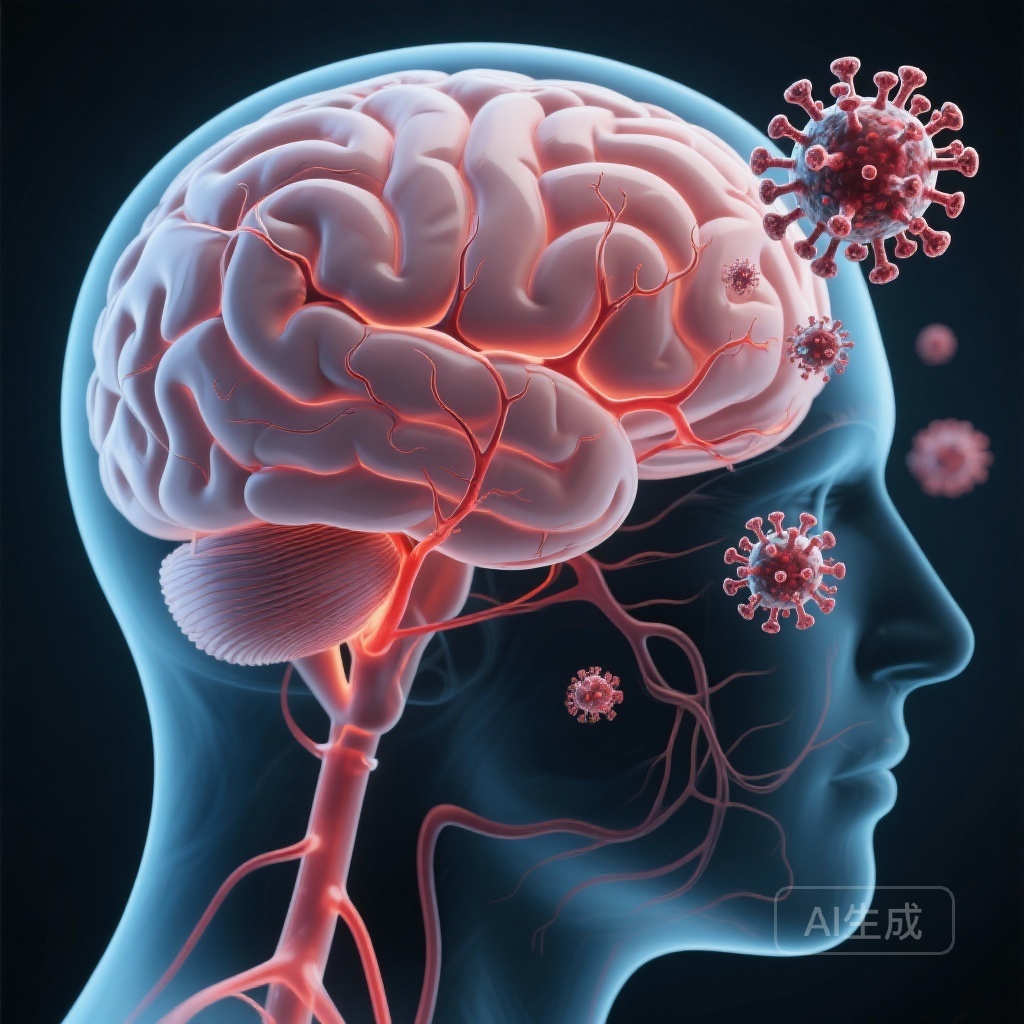
A large-scale population-based study in Singapore reveals that acute dengue virus infection is associated with a nearly ten-fold increase in neurological events, including memory loss and movement disorders, particularly in older adults and during specific serotype outbreaks.