Posted inCardiology news
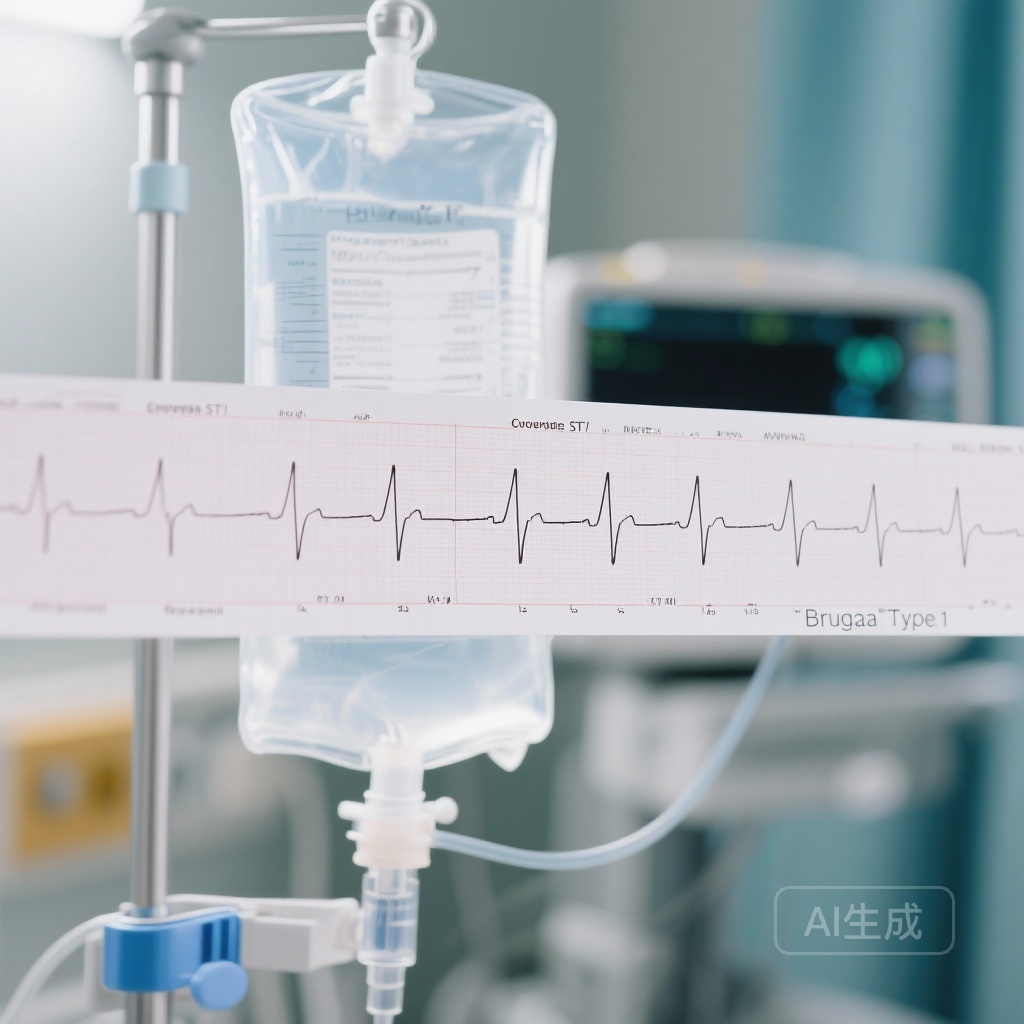
Procainamide Challenge for Brugada Syndrome: Establishing Diagnostic Safety and the Reassuring Prognosis of Induced Patterns
A large-scale registry study confirms that procainamide infusion is exceptionally safe for Brugada syndrome diagnosis, with high sensitivity and specificity. Crucially, asymptomatic patients with a procainamide-induced type 1 pattern demonstrate a very low risk of future arrhythmic events, potentially guiding more conservative management strategies.