Posted inInternal Medicine Neurology news
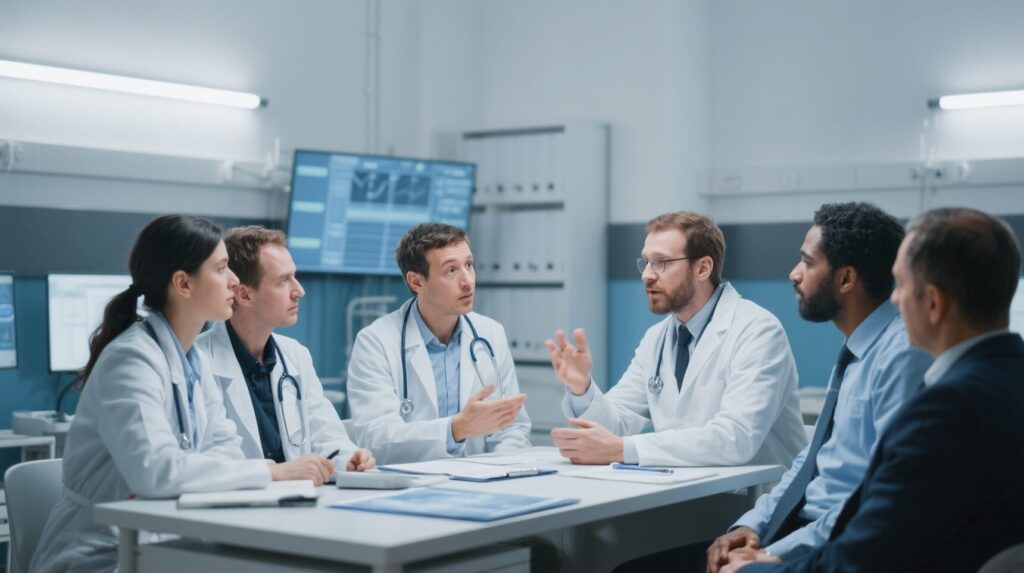
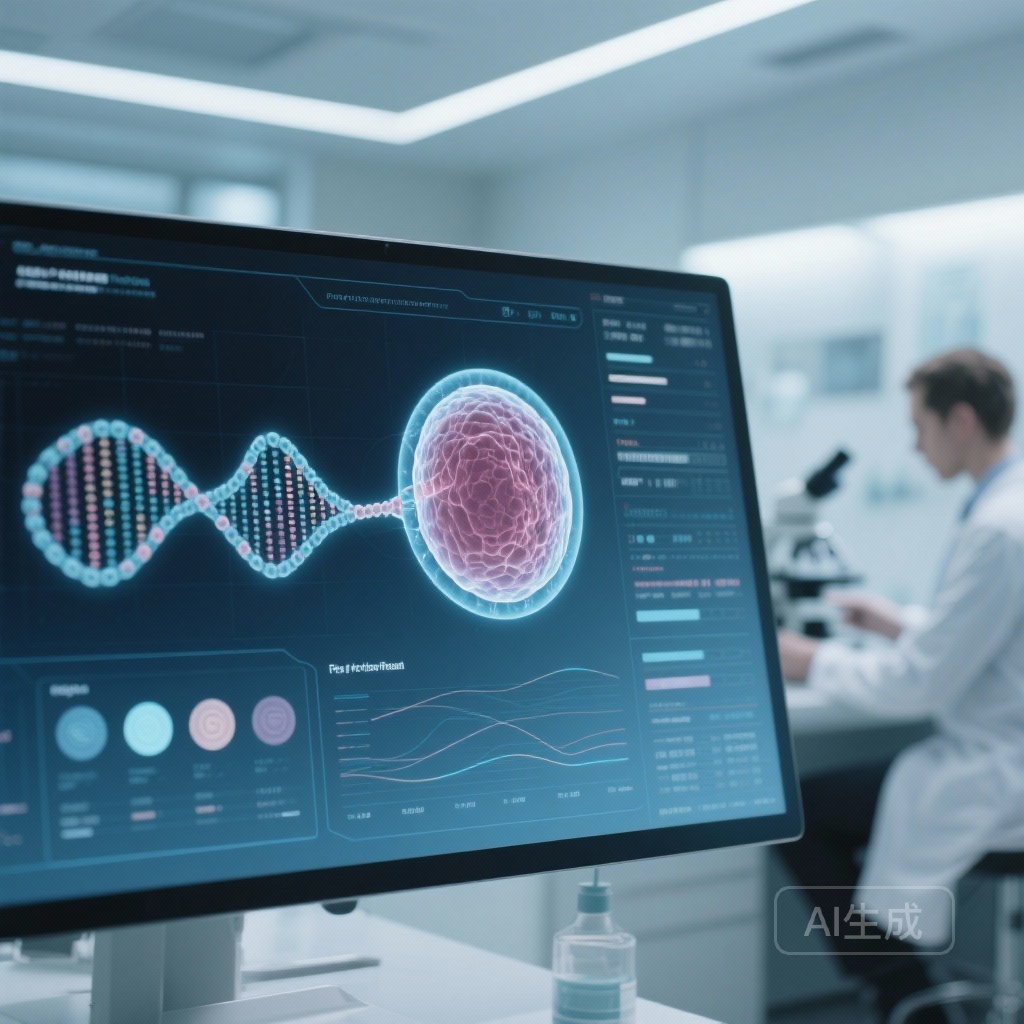
Blarcamesine in Early Alzheimer’s Disease: Promising Results Amidst Controversies
Blarcamesine shows potential in slowing early Alzheimer's progression, but questions about trial data robustness and transparency have been raised.