Highlight
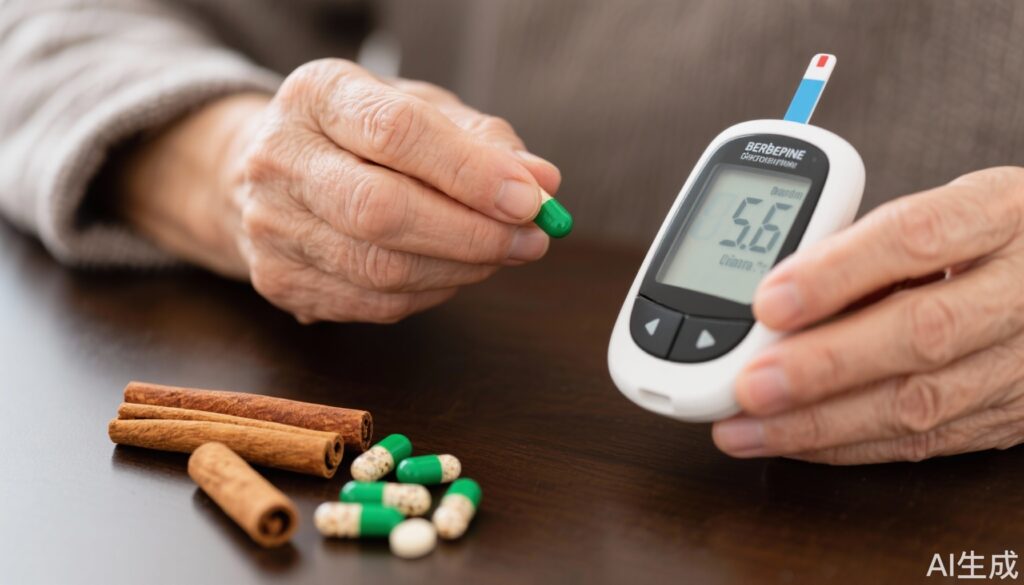
– Combined daily supplementation with 1200 mg berberine and 600 mg cinnamon for 12 weeks reduced fasting blood sugar (FBS) and HbA1c in type 2 diabetes patients.
– Significant reduction in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) was observed, although total cholesterol, HDL-C, and triglycerides remained unchanged.
– No significant changes were found in other metabolic or anthropometric parameters, indicating targeted metabolic benefits.
– The combined regimen was well tolerated with no reported adverse safety concerns.
Study Background and Disease Burden
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) represents a significant and growing global health challenge, associated with increased risk for microvascular complications (e.g., nephropathy, retinopathy) and macrovascular diseases (e.g., coronary artery disease, stroke). Effective management primarily hinges on controlling hyperglycemia and modifiable cardiometabolic risk factors such as dyslipidemia and hypertension to mitigate these risks. Despite advances in pharmacotherapy, many patients continue to struggle with suboptimal metabolic control or face side effects that limit adherence. Thus, novel or adjunctive therapeutic strategies, including complementary supplements with potential glucose- and lipid-lowering properties, are an appealing area of research.
Study Design
This investigation was a 12-week parallel, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of combined berberine and cinnamon supplementation in patients with T2DM. Eligible participants had established diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and were randomized to receive either a divided daily dose of 1200 mg berberine plus 600 mg cinnamon or an identical placebo. Primary endpoints included glycemic parameters (fasting blood sugar and HbA1c) and lipid profile indices. The investigators employed analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) to assess differences between groups at study end while adjusting for baseline values.
Key Findings
At the conclusion of the 12-week study, participants treated with berberine plus cinnamon exhibited statistically significant reductions in fasting blood sugar (P = 0.031) and HbA1c (P = 0.013) compared with placebo, indicating improved glycemic control. Additionally, a significant decrease in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels (P = 0.039) was noted in the supplementation group. However, total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and triglyceride levels did not significantly differ between groups, suggesting selective lipid-modulatory effects. Other metabolic parameters and anthropometric data did not show significant changes, indicating the intervention may specifically target glucose metabolism and LDL cholesterol.
The safety profile was favorable; no adverse events or safety concerns were reported related to the supplementation regimen. This supports the tolerability of combining berberine with cinnamon as an adjunctive therapy in diabetes management.
Expert Commentary
Berberine, a bioactive compound extracted from Berberis species, has been demonstrated in multiple studies to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), enhancing insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake. Similarly, cinnamon contains active polyphenols thought to improve insulin signaling and reduce oxidative stress. The synergistic effect observed may thus be rooted in complementary mechanisms of action targeting glucose metabolism and LDL cholesterol biosynthesis or clearance.
While these results are promising, the modest sample size and relatively short duration (12 weeks) of the trial suggest that larger, longer-term studies are warranted to confirm sustained efficacy and explore broader cardiovascular outcomes. Additionally, the lack of improvement in other lipid fractions or anthropometric measures calls for more comprehensive metabolic profiling to delineate the full impact of the supplement combination.
Conclusion
This rigorous randomized clinical trial provides evidence that 12 weeks of combined berberine and cinnamon supplementation can safely reduce fasting blood sugar, HbA1c, and LDL cholesterol levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. These findings support the therapeutic potential of this natural supplement pairing as an adjunct to conventional diabetes management, particularly for improving glycemic control and dyslipidemia. Future research should focus on confirming these benefits over longer periods and in diverse patient populations, as well as investigating mechanistic pathways and combined effects with established pharmacotherapies.
References
Mansour A, Sajjadi-Jazi SM, Gerami H, Khorasanian AS, Moalemzadeh B, Karimi S, Afrakoti NM, Mofid V, Mohajeri-Tehrani MR, Hekmatdoost A. The efficacy and safety of berberine in combination with cinnamon supplementation in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. Eur J Nutr. 2025 Feb 25;64(2):102. doi: 10.1007/s00394-025-03618-9